Articulation Disorder: Definition, Types, Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Overview and Explanation
Overview and Explanation
Imagine not being able to pronounce the words you want to say, no matter how hard you try. For individuals with Articulation Disorder, this is a daily struggle. Articulation Disorder, also known as Speech Sound Disorder, is a type of speech disorder that affects an individual’s ability to correctly pronounce sounds, syllables, or words. This condition can significantly impact one’s communication skills, social interactions, and overall quality of life.
Articulation Disorder is characterized by difficulties with articulation, referring to the physical process of producing speech sounds. This can include problems with movements of the lips, tongue, teeth, or palate. For example, a child with Articulation Disorder may have trouble saying the “r” sound, substituting it with a “w” sound instead, saying “wabbit” instead of “rabbit.” Similarly, an adult with the disorder may struggle to pronounce the “th” sound, saying “dis” instead of “this.”
Articulation Disorder can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, neurological disorders, hearing impairments, brain injuries, or developmental delays. In some cases, the exact cause may be unknown. Research suggests that between 2-10% of preschool-age children have some degree of Articulation Disorder.
One common example is a lisp, where an individual substitutes the “s” or “z” sound with a “th” sound; instead of saying “snake,” the person might say “thnake.” Another example is rhotacism, where there’s difficulty pronouncing the “r” sound, replacing it with a different sound or omitting it altogether.
Articulation Disorder can be classified into different types, depending on the nature of the speech difficulties. These include:
- Distortion: Where the individual produces a speech sound incorrectly, but the sound is still recognizable. For instance, a person might pronounce the “s” sound more like a “sh” sound.
- Substitution: Where the individual replaces one speech sound with another. For example, a child might say “t” instead of “c” or “d.”
- Omission: Where the individual leaves out a speech sound altogether, such as saying “no” instead of “snow.”
- Addition: Where the individual adds an extra speech sound. For instance, a person might say “hel-ruh-lo” instead of “hello.”
If left untreated, Articulation Disorder may lead to decreased self-confidence, social anxiety, and difficulties with educational and professional development. However, with the help of a speech-language pathologist (SLP), individuals with Articulation Disorder can learn to correct their speech patterns and improve their communication skills. Effective treatment may involve articulation therapy, tongue-twisters, and speech exercises.
Background and Context
Articulation Disorder, also known as Speech Sound Disorder, is a type of communication disorder affecting an individual’s production of speech sounds. It is estimated that around 10% of children and 5% of adults in the United States are affected. To understand this disorder's complexities, let’s delve into its background and context.
Defining Articulation Disorder
Articulation Disorder is a neurological condition that impairs a person’s ability to produce speech sounds accurately. This may manifest as substitutions, omissions, or distortions of sounds. A child might say “tat” instead of “cat” or “dawg” instead of “dog.” In some cases, the disorder may be developmental, while other times it may arise from a neurological or physical condition.
Prevalence and Risk Factors
Articulation Disorder is more prevalent in children than adults. According to the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA), approximately 10% of children in the U.S. have a speech sound disorder. Risk factors include:
- Family history of speech or language disorders
- Premature birth
- Neurological conditions such as cerebral palsy or Down syndrome
- Hearing loss or persistent ear infections
- Developmental delays or disabilities
Impact on Daily Life
Articulation Disorder can significantly affect communication, social interactions, and self-esteem. Imagine attempting to order food at a restaurant only to be met with confusion or frustration due to unclear speech. This can create significant stress for those affected.
Case Study: Timmy’s Story
Timmy, a 4-year-old boy, was diagnosed with Articulation Disorder after his parents noticed he was struggling to pronounce words. Even though he had normal hearing and intelligence, Timmy had difficulty with “r” and “l” sounds, replacing them with “w” sounds. With the help of a speech-language pathologist, Timmy began therapy and slowly improved his speech, boosting his confidence and ability to communicate with family and friends.
Addressing Articulation Disorder
Articulation Disorder is treatable with the help of a speech-language pathologist. Therapies may include:
- Articulation therapy: Targeting specific sounds to improve pronunciation
- Phonological awareness: Developing an understanding of sounds
- Language therapy: Building communication skills and vocabulary
Understanding Articulation Disorder helps appreciate the complexities and the importance of early intervention. In the next section, we will explore the symptoms and characteristics in more detail.
Related Terms and Concepts
Articulation Disorder is often intertwined with other speech and language difficulties, making it essential to understand related terms and concepts. This section delves into connections between Articulation Disorder and other conditions, therapies, and techniques.
1. Apraxia of Speech (AOS)
Apraxia of Speech is a neurologically-based speech disorder impacting coordination of muscles used for speech. While Articulation Disorder primarily focuses on sound production, AOS affects the brain's ability to plan and execute speech movements. Both conditions often co-occur, making understanding their distinctions crucial for effective treatment.
Case Study: Emily, a 4-year-old, was diagnosed with both Articulation Disorder and AOS. Her speech therapist worked with her to develop correct articulation skills alongside AOS-targeted exercises.
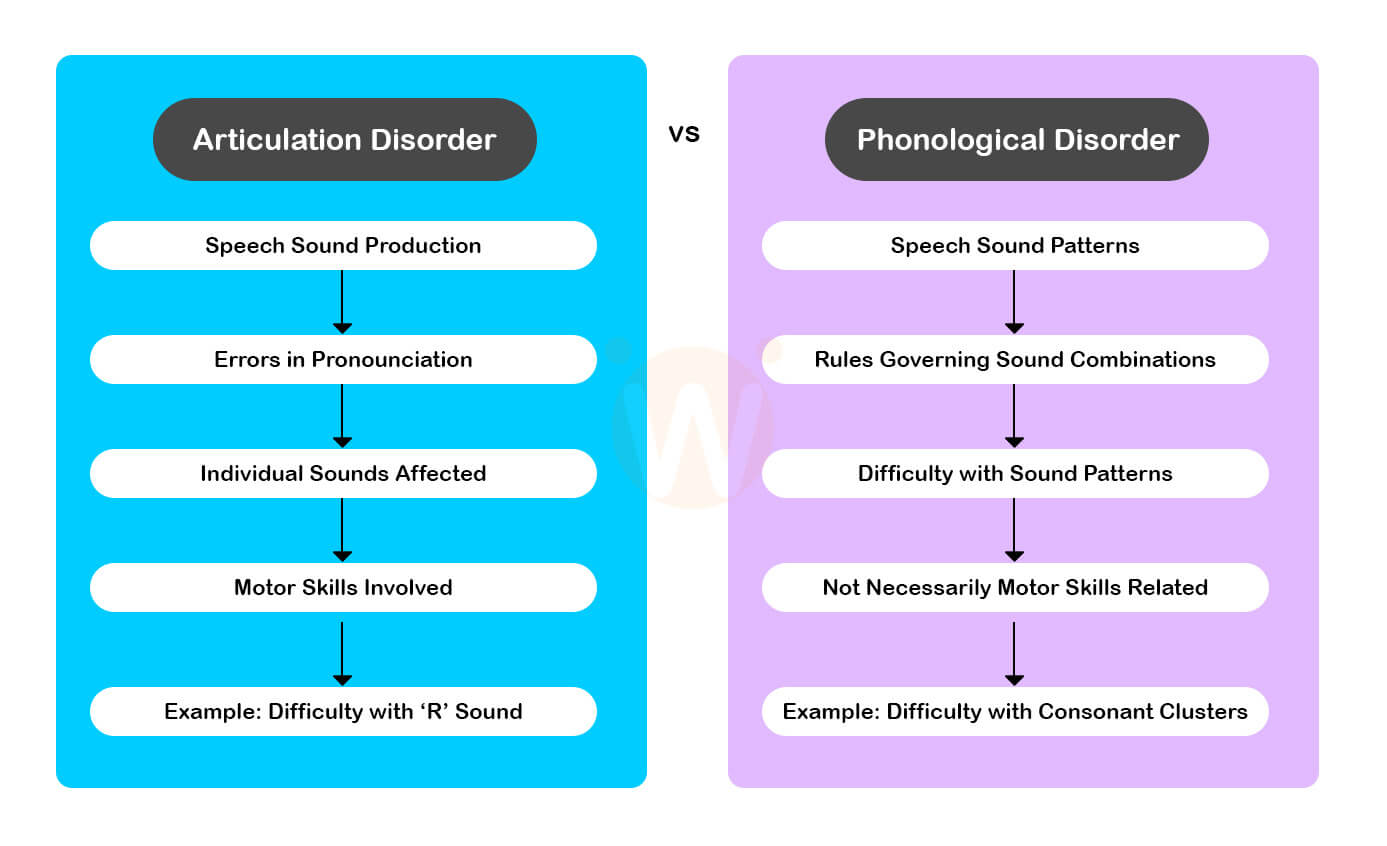
2. Phonological Disorder
Phonological Disorder affects sound use consistency within speech sounds. Unlike Articulation Disorder, which focuses on individual sounds, Phonological Disorder involves patterns of sound use. Articulation therapists work with individuals affected to improve these sound patterns.
3. Dysarthria
Dysarthria is a speech disorder caused by nerve damage or muscle weakness. This affects a person’s ability to produce clear and coherent speech, encompassing articulation, prosody, and voice quality difficulties.
4. Speech Sound Disorder (SSD)
Speech Sound Disorder encompasses a range of speech sound difficulties, including Articulation Disorder. SSD may involve sound production difficulties or sound patterns.
5. Oro-Myo-Functional (OMF) Therapy
Oro-Myo-Functional Therapy focuses on developing articulation skills through exercises targeting the muscles used for speech. This therapy is often used alongside traditional approaches to address Articulation Disorder.
By understanding these related terms and concepts, individuals with Articulation Disorder can navigate the therapeutic process better and achieve optimal communication outcomes.
Practical Examples and Case Studies
Articulation disorders manifest uniquely in each individual. Let’s explore practical examples and case studies to better comprehend articulation disorders.
Case Study 1: The Misadventures of “Th” Sounds
Meet Emma, a bright 6-year-old who loves playing with friends. However, when Emma attempts to say “this” or “that,” it comes out as “dis” or “dat.” Her speech-language pathologist identifies the issue and develops a customized treatment plan focusing on articulating the “th” sound.
Through targeted exercises like tongue twisters and word repetition, Emma gradually improves her ability to articulate. With practice, Emma gains confidence in communication, making her peers understand her better.
Case Study 2: Overcoming Apraxia
Alex, a 4-year-old boy diagnosed with childhood apraxia of speech (CAS), struggles to articulate even simple words. His SLP creates a treatment plan incorporating gestures, pictures, and AAC devices.
With consistent practice and therapy sessions, Alex develops awareness of his articulatory movements. He learns to break words into smaller sounds, gradually vocalizing. With family support and SLP guidance, Alex makes substantial progress, enhancing his overall communication.
Case Study 3: Integrating Multilingual Articulation Goals
Sofia, a 7-year-old from a bilingual household, often switches between languages but struggles with the /r/ sound in both. Her SLP recognizes the need for a multilingual treatment plan to address articulation in English and Spanish.
The SLP develops a plan targeting the /r/ sound in both languages, utilizing multilingual materials and parent-child interaction therapy. This approach enhances Sofia’s communication skills across languages.
Practical Strategies for Parents and Caregivers
While every individual has unique needs, here are several practical strategies for parents and caregivers to support their loved ones:
- Practice regularly: Consistent practice can help improve communication skills.
- Visual aids: Use pictures, charts, and diagrams to enhance understanding.
- Make it enjoyable: Incorporate games and activities that promote practice.
- Collaborate with your SLP: Work with your SLP to develop a customized treatment plan addressing specific goals.
- Support multilingual communication: Utilize multilingual materials and interaction therapy for effective communication.
By exploring these examples, one gains a deeper understanding of articulation disorders and the importance of tailored treatment plans. Whether you’re a parent, caregiver, or SLP, these insights can help individuals with articulation disorders promote confident communication.
Symptoms and Signs
Articulation disorder, also known as speech sound disorder, affects the production of sounds, syllables, or words correctly. Symptoms may vary based on severity, type, and underlying causes.
Types of Articulation Errors
- Substitution: Replacing one sound with another (e.g., saying “tat” instead of “cat”)
- Omission: Leaving out a sound (e.g., saying “ca” instead of “cat”)
- Distortion: Altering the way a sound is pronounced (e.g., saying “shat” instead of “cat”)
- Addition: Adding an extra sound (e.g., saying “cacak” instead of “cat”)
Common Signs of Articulation Disorder
- Difficulty with word pronunciation: Struggling to pronounce words correctly, such as saying “wabbit” instead of “rabbit.”
- Struggling to communicate effectively: Difficulty expressing thoughts due to unclear speech.
- Frustration or embarrassment: Feeling self-conscious about speaking.
- Avoiding certain words or sounds: Steering clear of words that are difficult to pronounce.
- Misunderstandings: Frequent confusion or miscommunication due to unclear speech.
Real-Life Examples
- Case study: Emily, a 4-year-old girl, struggles with the “r” sound, saying “wabbit” instead of “rabbit.” Her avoidance of “r” words is evident.
- Personal story: John, a 30-year-old, has a lisp and often says “thith” instead of “this.” He has adapted by using alternative phrases.
Articulation disorder may co-occur with other conditions:
- Language disorder: Issues with vocabulary or grammar.
- Fluency disorder: Stuttering or stammering.
- Voice disorder: Problems with vocal tone or volume.
- Learning disabilities: Difficulties in reading or academic skills.
Seeking Help
If you or a loved one shows symptoms of articulation disorder, seek guidance from a speech-language pathologist (SLP). An SLP can assess, identify underlying causes, and develop a personalized treatment plan. Early intervention significantly impacts treatment effectiveness, so do not hesitate to seek help.
Treatment and Therapy Options
Receiving an Articulation Disorder diagnosis can be challenging, but the right treatment can improve communication skills and quality of life. The primary goal is to address the difficulties that hinder proper speech production, allowing clear communication.
Speech Therapy: The Cornerstone of Treatment
Speech therapy effectively addresses Articulation Disorders. A speech-language pathologist (SLP) works closely with individuals, assessing severity, identifying needs, and developing personalized treatment plans. Techniques may include:
- Articulation therapy: Teaching correct production of problematic sounds.
- Phonological therapy: Targeting underlying patterns causing difficulties.
- Apraxia therapy: Sequencing sounds and syllables for those with apraxia.
For instance, a preschooler who says “wabbit” instead of “rabbit” might play “Rabbit’s Garden” to practice the “r” sound in a fun context, helping them develop the necessary muscle memory.
Additional Treatment Approaches
- Oral-motor therapy: Strengthening mouth, tongue, and lips for better articulation.
- Hearing aids: For individuals with hearing loss which may contribute to articulation issues.
- Parent-child interaction therapy: Engaging parents to support their child’s communication development.
Technology-Enhanced Therapy
Technology can enhance treatment, offering interactive tools:
- Speech-generating devices: For effective communication.
- Mobile apps: Interactive games for engaging practice, such as articulation apps.
- Virtual therapy: Remote access to speech therapy, broadening treatment access.
Collaborative Care
A multidisciplinary approach is vital for addressing Articulation Disorders. SLPs may collaborate with:
- Audiologists: For addressing hearing difficulties.
- Occupational therapists: Supporting fine motor or cognitive challenges.
- Psychologists: Addressing emotional factors comprehensively.
This collaborative approach can significantly help individuals meet their communication goals.
Developmental and Childhood Context
Articulation disorder affects an individual’s ability to produce sounds. In childhood, it can impact effective communication and meaningful relationships.
Early Warning Signs
Initially, articulation disorder may be masked by limited vocabulary, yet as children develop, these errors become more evident.
A child may show early warning signs, including:
- Interdental lisp, where the tongue is between the teeth.
- Difficulty articulating sounds like “r,” “l,” “s,” and “z.”
- Replacing sounds with similar but incorrect sounds.
- Altered speech patterns such as slurred or slow speech.
The Importance of Early Intervention
Early intervention is crucial for addressing articulation disorders in children. Untreated, these disorders can lead to negative consequences, including:
- Low self-esteem
- Social relationship difficulties
- Academic struggles in reading and writing
- Emotional problems
Research indicates significant improvements with early therapy, underscoring the need for prompt action.
Case Study: Timmy’s Story
Timmy, diagnosed with an articulation disorder, struggled with the “r” sound. Through targeted therapy, incorporating visual, auditory, and kinesthetic activities, he made substantial advances in just six months, significantly improving his communication skills.
Long-Term Implications
In conclusion, addressing articulation disorder in childhood is pivotal for social, emotional, and academic growth. Early intervention and tailored therapy can enhance speech and overall communication abilities for a lifetime of effective interaction.
This explanation highlights important keywords such as “articulation disorder,” “child development,” and “speech therapy,” improving online visibility.
Important Sources
| Articulation Disorder: What It Is, Types & Treatment - Cleveland Clinic | Articulation disorder is a common condition when your child can’t make specific sounds. For example, they may always replace “r” with “w” or “th” with “s.” The disorder isn’t related to any issues with their brain, mouth or hearing. |
| Speech Sound Disorders-Articulation and Phonology | Articulation disorders focus on errors (e.g., distortions and substitutions) in production of individual speech sounds. Phonological disorders focus on predictable, rule-based errors (e.g., fronting, stopping, and final consonant deletion) that affect more than one sound. |
| Articulation Disorder: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments | Articulation Disorder: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments. Articulation disorder begins in childhood but can last into adulthood if left untreated. This article addresses the top questions about articulation disorder, including symptoms and treatment options for … |
| Speech disorders: Types, symptoms, causes, and treatment | A speech disorder is any condition that affects a person’s ability to produce sounds that create words. Damage to muscles, nerves, and vocal structures can cause it. Examples include... |
| Speech Impairment: Types, Signs & Causes - Cleveland Clinic | A speech impairment (sometimes called a speech impediment or speech disorder) happens when you have trouble saying sounds so that people don’t understand what you’re saying. Some people are born with conditions that affect their speech. |
| Speech disorders: Types, Symptoms, Causes, and More - Healthline | Some people with speech disorders are aware of what they would like to say but unable to articulate their thoughts. This may lead to self-esteem issues and the development of depression. Speech... |
| Speech and Language Disorders - Symptoms and Causes - Penn … | A speech disorder is a condition in which a person has problems creating or forming the speech sounds needed to communicate with others. This can make the child's speech difficult to understand. Common speech disorders are: Articulation disorders. Phonological disorders. Disfluency. Voice disorders or resonance disorders. |
| The SLP’s Guide to Speech Sound Disorders: Articulation & Phonological ... | What is an articulation disorder? An articulation disorder is characterized by difficulty producing individual speech sounds. The impairment is at the phonetic/motoric level, meaning that a sound may be substituted or distorted in a predictable way. Example: A student produces the /s/ and /sh/ sounds with lateral airflow (e.g., a lateral lisp). |
| Speech problems – articulation and phonological disorders | A child with an articulation disorder has problems forming speech sounds properly. A child with a phonological disorder can produce the sounds correctly, but may use them in the wrong place. When young children are growing, they develop speech sounds in a predictable order. |
| Articulation Disorders: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment - Better Speech | Articulation disorders are speech difficulties that hinder an individual's ability to produce certain sounds correctly. These disorders can affect communication skills and social interactions, significantly impacting one's quality of life. |